Chapter 10 Review Test 5th Grade Answer Key
Go gratis pace by step explanations for all the questions in Go Math Grade 7 Answer Key Affiliate 10 Random Samples and Populations. Make use of the links and start preparing for the exams through Get Math Grade 7 Answer Central for Affiliate 10 Random Samples and Populations. It is very essential for the students to empathize the concepts in Chapter ten Random Samples and Populations.
Go Math Form seven Answer Fundamental Affiliate ten Random Samples and Populations
Get Math Grade seven Solution Key Chapter 10 Random Samples and Populations is the best study textile to score the highest marks in the examinations. The HMH Go Math seventh Grade Respond Central Affiliate 10 Random Samples & Populations helps the students to understand the concepts without any difficulty. Click on the below links for the Go Math Grade vii solutions which are given with a cursory explanation.
Chapter x Random Samples and Populations – Lesson 1
- Guided Practice – Folio No. 314
- Independent Practice – Page No. 315
- H.O.T. – Page No. 316
Chapter x Random Samples and Populations – Lesson: 2
- Guided Exercise – Page No. 320
- Independent Exercise – Page No. 321
- Page No. 322
Affiliate 10 – Random Samples and Populations
- Page No. 326
- Page No. 327
- Folio No. 328
- ten.ane Populations and Samples – Page No. 329
- Selected Response – Page No. 330
Guided Practice – Page No. 314
Question i.
Follow each method described below to collect data to estimate the boilerplate shoe size of seventh grade boys.
Respond:
Method 1:
Select randomly 5 seventh form boys and record their shoe size in a table.
Respond:
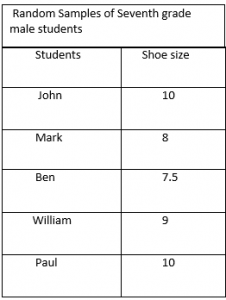
The mean is \(\frac{ten+viii+7.v+9+10}{5}
= \frac{44.5}{five}\)
= 8.9
Method 2:
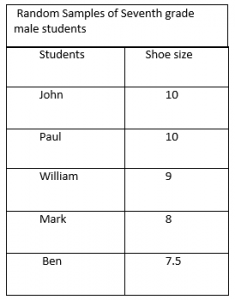
Notice the 5 boys in the class who has largest shoe size and record in a table.
Answer:
Question two.
Method 1 produces results that are more/less representative of the entire student population because information technology is a random/biased sample.
Respond: Method ane produces results that are more than representative of the entire student population because it is a random sample.
Question 3.
Method two produces results that are more/less representative of the unabridged educatee population because it is a random/biased sample.
Answer: Method ii produces results that are less representative of the unabridged student population because it is a biased sample.
Question 4.
Heidi decides to use a random sample to determine her classmates' favorite color. She asks, "Is greenish your favorite colour?" Is Heidi's question biased? If so, give an instance of an unbiased question that would serve Heidi better.
Respond: Heidi's question is biased every bit it suggests that people should say their favorite color is dark-green. "What was your favorite colour?" is an unbiased question, as it doesn't suggest a certain answer.
Essential Question Check-In
Question 5.
How can you select a sample so that the information gained represents the entire population?
Answer: Nosotros should select a sample that is randomly chosen and is sufficiently large enough so that the result so that results are representative of the entire population.
Contained Practice – Page No. 315
Question 6.
Paul and his friends average their test grades and find that the average is 95. The teacher announces that the average grade of all of her classes is 83. Why are the averages so different?
Answer: As Paul and his friends are non a randomly chosen sample of the class population, so the averages are unlike.
Question 7.
Nancy hears a report that the average price of gasoline is $two.82. She averages the prices of stations nearly her home. She finds the average toll of gas to be $iii.03. Why are the averages dissimilar?
Answer: The gas stations effectually Nancy home are not a randomly chosen sample of all gas stations in the land, so the averages are then different.
For 8–10, determine whether each sample is a random sample or a biased sample. Explain.
Question viii.
Ballad wants to detect out the favorite foods of students at her middle school. She asks the boys' basketball game team about their favorite foods.
Answer: Equally Carol asks merely boys and girls are not represented in the sample, so the sample is biased.
Question 9.
Dallas wants to know what constituent subjects the students at his school like best. He surveys students who are leaving band class.
Reply: Dallas asked only students who are in ring class and elective subject students are not represented, and then the sample is biased.
Question 10.
To choose a sample for a survey of seventh graders, the student quango puts pieces of newspaper with the names of all the seventh graders in a bag, and selects 20 names.
Answer: As all students had an equal take a chance of being represented in the survey, and so the sample is random.
Question xi.
Members of a polling arrangement survey 700 of the 7,453 registered voters in a town by randomly choosing names from a list of all registered voters. Is their sample probable to be representative?
Reply: The sample is large enough and randomly chosen from all registered voters so that every voter gets a chance of beingness selected.
So the sample is likely to be representative.
For 12–13, determine whether each question may be biased. Explicate.
Question 12.
Joey wants to find out what sport seventh form girls like most. He asks girls, "Is basketball your favorite sport?"
Answer: As information technology mentions basketball and suggesting that girls should give a certain answer. So the question is biased.
Question 13.
Jae wants to detect out what type of art her fellow students enjoy most. She asks her classmates, "What is your favorite blazon of art?"
Answer: As information technology does not suggest students should give a sure answer, so it is not biased.
H.O.T. – Folio No. 316
Focus on Higher Guild Thinking
Question xiv.
Draw Conclusions
Determine which sampling method will amend stand for the entire population. Justify your reply.
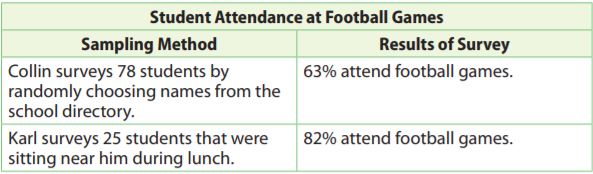
Reply: Collin's survey is a amend sampling method. Collin is randomly choosing names from the school directory, and then each pupil has a take chances of being chosen because they all announced in the school directory.
Karl's survey is biased, as he is but choosing the students that were sitting nearly him during lunch which means the people he is asking are non representative of the entire population.
Question fifteen.
Multistep
Barbara surveyed students in her school past looking at an alphabetical list of the 600 student names, dividing them into groups of x, and randomly choosing one from each group.
a. How many students did she survey? What type of sample is this?
__________ people
This is a __________ sample
Answer: Barbara fabricated 600÷x= sixty groups, so she chosen one person in each grouping and surveyed 60 people. Then this is a random sample considering all the students are beingness represented and accept an equal take a chance of beingness called.
Question 15.
b. Barbara found that 35 of the survey participants had pets. About what percent of the students she surveyed had pets? Is information technology safe to believe that about the same per centum of students in the school take pets? Explain your thinking.
__________ %
Answer: Equally there are 60 survey participants and in that 35/60= 0.58% ≈58%. Yes, information technology is rubber to believe that virtually the same per centum of students in the schoolhouse have pets because the sample is large plenty large and all students accept represented.
Question 16.
Communicating Mathematical Ideas
Carlo said a population can have more one sample associated with it. Exercise you hold or disagree with his argument? Justify your answer.
Answer: Yeah I agree. Equally there are many dissimilar ways to randomly select a sample. By using the same fashion of choosing a sample multiple times could create a unlike sample. For example, picking name out of a chapeau will non give you the same sample every fourth dimension since the names will go mixed up every time you go to pick a proper noun.
Guided Practice – Page No. 320
Patrons in the children'southward section of a local branch library were randomly selected and asked their ages. The librarian wants to use the data to inferthe ages of all patrons of the children'south section so he tin select age appropriate activities. In three–half-dozen, complete each inference.
vii, 4, 7, 5, 4, x, eleven, half dozen, vii, 4
Question 1.
Make a dot plot of the sample population data.
Answer:
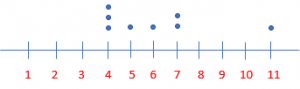
Question two.
Brand a box plot of the sample population data.
Answer: First we demand to find the median, so nosotros need to order the numbers from least to greatest: 4,four,4,five,vi,7,7,7,10,11.
So median is (vi+7)/two= 13/2= 6.5.
And the median for half of the information is 4,four,iv,five,half-dozen= iv.
And the other half of the information is 7,7,7,10,eleven= vii.
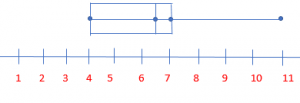
Question three.
The virtually common ages of children that apply the library are _____ and _____.
_____ and _____
Answer: four and 7 are the numbers repeated the most in the information set, so the most common ages of the children that use the library are 4 and 7.
Question 4.
The range of ages of children that employ the library is from _____ to _____.
_____ to _____
Answer: The lower that appears in the data set is 4 and the higher that appears in the data set is xi, then the range of ages of children that use the library is from 4 to 7.
Question 5.
The median age of children that use the library is _____.
_____
Respond: The median historic period of children that use the library is 6.5.
Question 6.
A manufacturer fills an social club for iv,200 smart phones. The quality inspector selects a random sample of 60 phones and finds that 4 are lacking. How many smart phones in the order are probable to be defective?
Nearly _____ smart phones in the social club are likely to be lacking.
_____ smartphones
Answer: If we breakdown the whole order into samples of 60 phones we volition go 4200÷sixty= 70 samples. Then if we find 4 defective smartphones in every sample and nosotros can expect well-nigh 4×70= 280 smartphones in the order are probable to be defective.
Question 7.
Role of the population of 4,500 elk at a wild animals preserve is infected with a parasite. A random sample of fifty elk shows that viii of them are infected. How many elk are probable to be infected?
_____ elk
Reply: If we pause down the whole elk population into samples of l elk, nosotros get 4500÷fifty= 90 samples. So if we find viii infected elk in every sample and we can expect well-nigh 8×90= 720 elk to be infected.
Essential Question Check-In
Question 8.
How can you use a random sample of a population to brand predictions?
Reply: Nosotros can employ a random sample of a population to brand predictions by setting the ratio for the sample equal to the ratio for the population.
Contained Practise – Page No. 321
Question 9.
A director samples the receipts of every 5th person who goes through the line. Out of 50 people, 4 had a mispriced particular. If 600 people go to this shop each twenty-four hours, how many people would you expect to take a mispriced detail?
_____ people
Answer: 48 people.
Explanation:
Allow 10 be the number of people with a mispriced item, so
4/l= X/600
50X= 2400
X= 48.
So there will be 48 people with a mispriced item.
Question 10.
Jerry randomly selects 20 boxes of crayons from the shelf and finds 2 boxes with at least one broken crayon. If the shelf holds 130 boxes, how many would you lot expect to have at to the lowest degree ane broken crayon?
_____ boxes
Respond: xiii boxes.
Caption:
Let X exist the number of boxes with at least 1 cleaved crayon
2/20= X/130
20X= 260
10= thirteen.
So at that place volition be 13 boxes with at least ane cleaved crayon.
Question 11.
A random sample of dogs at unlike animal shelters in a city shows that 12 of the threescore dogs are puppies. The metropolis'due south creature shelters collectively house 1,200 dogs each year. About how many dogs in all of the metropolis'due south animate being shelters are puppies?
_____ dogs
Answer: 240 dogs.
Caption:
Permit X be the number of boxes with at least 1 cleaved crayon
12/60= X/1200
60X= 14400
Ten= 240.
And so in that location will be 240 dogs in all of the urban center's animal shelters are puppies.
Question 12.
Part of the population of 10,800 hawks at a national park are building a nest. A random sample of 72 hawks shows that 12 of them are building a nest. Estimate the number of hawks edifice a nest in the population.
_____ hawks
Answer: 1800 hawks.
Explanation:
Allow X be the number of boxes with at least one broken crayon
12/72= X/10,800
72X= 10,800
X= 1800.
And then there will be 1800 number of hawks building a nest in the population.
Question thirteen.
In a wild fauna preserve, a random sample of the population of 150 raccoons was defenseless and weighed. The results, given in pounds, were 17, 19, 20, 21, 23, 27, 28, 28, 28 and 32. Jean made the qualitative statement, "The boilerplate weight of the raccoon population is 25 pounds." Is her statement reasonable? Explain.
_____
Answer: Aye, Jean'southward argument is reasonable.
Caption: Equally the weights are not given for all 150 raccoons, so we don't know how many raccoons at each of the weights given and we cannot calculate the boilerplate. And then the best way to judge the average is to find the median of the information fix. And so the median is
(23+27)/2= 25. Equally the median is 25 Jean'south statement is reasonable.
Question fourteen.
Greta collects the number of miles run each week from a random sample of female marathon runners. Her data are shown below. She made the qualitative statement, "25% of female marathoners run 13 or more miles a calendar week." Is her statement reasonable? Explain. Data: 13, 14, 18, 13, 12, 17, 15, 12, thirteen, 19, 11, fourteen, xiv, eighteen, 22, 12.
_____
Reply: Greta'southward statement is not reasonable.
Explanation: If we fix the data from least to highest and so eleven,12,12,12,13,13,13,14,14,xiv,15,17,18,18,19,22. So there are 16 marathon runners, 12 of them run thirteen miles or more each week. So
12/16= 0.75= 75%. So Greta'southward statement is not reasonable.
Question xv.
A random sample of 20 of the 200 students at Garland Simple is asked how many siblings each has. The data are ordered as shown. Make a dot plot of the data. Then make a qualitative argument about the population. Information: 0, one, 1, 1, 1, one, ane, 2, two, ii, two, 2, 3, three, 3, 3, four, four, four, 6.
Respond: The mean is ii.
Explanation:
The mean is \(\frac{0+one+1+1+1+ane+1+2+2+2+2+2+three+3+iii+iii+four+4+4+6}{xx}
= \frac{46}{20}\)
= 2.3
And then the mean is two equally for the siblings the number must be whole number.
Most of the students have at least 1 sibling and virtually of the students have fewer than half dozen siblings, and the students have an average of two siblings.
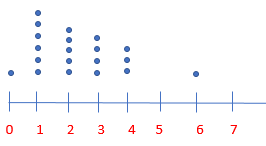
Question 16.
Linda collects a random sample of 12 of the 98 Wilderness Club members' ages. She makes an inference that most wilderness club members are between xx and 40 years old. Describe what a box plot that would confirm Linda's inference should look like.
Respond: Linda volition conclude that most of the society members are between the ages of 20 and forty, so more than half of the 12 surveyed members must be betwixt those ages. The box plot would have the lower quartile at twenty and upper quartile at twoscore.
Folio No. 322
Question 17.
What's the Error?
Kudrey was making a box plot. He offset plotted the to the lowest degree and greatest data values. He then divided the distance into half, and then did this again for each one-half. What did Kudrey do wrong and what did his box plot expect like?
Reply: By creating a box plot, the 3 eye values are not found by dividing the distance between the maximum and minimum values and then dividing the distances in one-half again. The iii middle values are found past finding the median of the set values, the median of the starting time half of the values, and the median of the final half of the values.
H.O.T.
Focus on Higher Order Thinking
Question eighteen.
Communicating Mathematical Ideas
A dot plot includes all of the actual information values. Does a box plot include any of the actual information values?
______
Answer: Yes, a dot plot will include all of the actual information values. The only actual data values that a box plot must have the minimum and maximum values. The three median values may are may not exist actual information values.
Question xix.
Brand a Conjecture
Sammy counted the peanuts in several packages of roasted peanuts. He found that the numberless had 102, 114, 97, 85, 106, 120, 107, and 111 peanuts. Should he make a box plot or dot plot to represent the data? Explain your reasoning.
______
Answer: Sammy should make a box plot to represent the data. As dot plots are helpful in finding the number of times each value occurs in a information ready. As the values occur merely one time, then the box plot volition better stand for the data.
Question 20.
Represent Real-Earth Problems
The salaries for the eight employees at a pocket-sized visitor are $twenty,000, $20,000, $22,000, $24,000, $24,000, $29,000, $34,000 and $79,000. Make a qualitative inference nearly a typical bacon at this company. Would an advertizement that stated that the average salary earned at the company is $31,500 exist misleading? Explain.
______
Answer: Yeah, the statement is misleading.
Explanation: The median of the data set is \(\frac{$24,000+$24,000}{2}
= \frac48,000}{2}\)
= 24,000.
Yep, the statement is misleading because $31,500 is higher than six of the 8 salaries at the company.
Page No. 326
A manufacturer gets a shipment of 600 batteries of which 50 are lacking. The store manager wants to exist able to test random samples in future shipments. She tests a random sample of 20 batteries in this shipment to see whether a sample of that size produces a reasonable inference almost the entire shipment.
Question i.
The manager selects a random sample using the formula randInt( , ) to generate _____ random numbers.
Answer: Since l out of 600 batteries are defective and she is testing twenty batteries she tin can use randInt(1,600) to generate 20 random numbers.
Question ii.
She lets numbers from ane to _____ represent defective batteries, and _____ to _____ represent working batteries. She generates this list: 120, 413, 472, 564, 38, 266, 344, 476, 486, 177, 26, 331, 358, 131, 352, 227, 31, 253, 31, 277.
Answer: She lets numbers from 1 to 50 represent lacking batteries and 51 to 600 represent working batteries. She generates this list:
120, 413, 472, 564, 38, 266, 344, 476, 486, 177, 26, 331, 358, 131, 352, 227, 31, 253, 31, 277.
Question three.
Does the sample produce a reasonable inference?
______
Answer: No, the sample does non produce a reasonable inference. In sample 26, 31,31,38 numbers represent defective batteries, and in shipment fifty out of 600 of the batteries are defective.
Essential Question Cheque-In
Question 4.
What can happen if a sample is likewise small or is not random?
Answer: If the sample is besides small or not random, it is likely to produce unrepresentative data values.
Folio No. 327
Maureen owns three bagel shops. Each shop sells 500 bagels per solar day. Maureen asks her store managers to use a random sample to see how many whole-wheat bagels are sold at each store each 24-hour interval. The results are shown in the table. Use the table for 5–7.
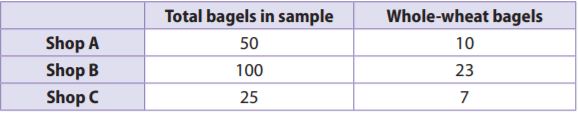
Question 5.
If y'all assume the samples are representative, how many whole-wheat bagels might yous infer are sold at each store?
Store A: ___________
Store B: ___________
Shop C: ___________
Reply:
Store A: 100.
Shop B: 115.
Shop C: 140.
Caption:
Shop A:
10/50×500
= 10×10
= 100.
Shop B:
23/100×500
= 23×5
= 115.
Shop C:
7/25×500
= vii×20
= 140.
Question 6.
Rank the samples for the shops in terms of how representative they are likely to be. Explain your rankings.
Answer: The samples can be ranked as C, A, B from least to virtually. Store B's is the most representative because information technology contained the well-nigh bagel. Store C's is the to the lowest degree representative considering it independent the fewest bagels.
Question seven.
Which sample or samples should Maureen utilise to tell her managers how many whole-wheat bagels to make each day? Explicate.
Respond: Maureen should use either Shop A or Shop B because the employ a sufficient number of bagels to be considered authentic. Shop C's sample would be the least representative because it independent the fewest bagels.
Question 8.
In a shipment of 1,000 T-shirts, 75 do not meet quality standards. The table beneath simulates a manager's random sample of 20 T-shirts to inspect. For the simulation, the integers 1 to 75 represent the below-standard shirts.
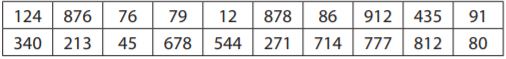
Answer: In the sample, two values are from ane to 75. So, 2 shirts are below the quality standards. And so
= 2/20×1000
= 2×50
= 100.
The prediction would be that 100 shirts are beneath quality standards, which would be 25 more than the actual number.
Folio No. 328
Question 9.
Multistep
A 64-acre coconut subcontract is arranged in an 8-by-eight array. Mika wants to know the boilerplate number of coconut palms on each acre. Each cell in the table represents an acre of country. The number in each cell tells how many coconut palms abound on that particular acre.
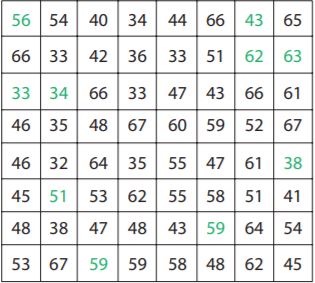
a. The numbers in green correspond Mika'south random sample of 10 acres. What is the boilerplate number of coconut palms on the randomly selected acres?
______
Answer: The average is 49.8 coconut palms.
Explanation: The average is \(\frac{56+43+62+63+33+34+38+51+59+59}{10}
= \frac{498}{10}\)
= 49.8
Question 9.
b. Project the number of palms on the unabridged farm.
______
Answer: 3187 palms.
Explanation: Every bit the boilerplate is 49.eight for each acre, and then for 64 acres information technology is 64×49.viii= 3187.2. So the number of palms on the entire farm is 3187.
H.O.T.
Focus on Higher Order Thinking
Question 10.
Draw Conclusions
A random sample of xv of the 78 competitors at a middle school gymnastics competition are asked their height. The data set lists the heights in inches: 55, 57, 57, 58, 59, 59, 59, 59, 59, 61, 62, 62, 63, 64, 66. What is the mean height of the sample? Practise you lot remember this is a reasonable prediction of the hateful meridian of all competitors? Explain.
Answer: Yes, this is a reasonable prediction.
Explanation: The mean height is \(\frac{55+57+57+58+59+59+59+59+59+61+62+62+63+64+66}{15}
= \frac{900}{fifteen}\)
= 60 inches.
Yep, this is a reasonable prediction of the mean height of all competitors because it is a good sample generated randomly and contains sufficient values. And then it should provide a practiced estimate of the hateful meridian of all competitors.
Question xi.
Disquisitional Thinking
The six-past-six grid contains the ages of actors in a youth Shakespeare festival. Describe a method for randomly selecting viii cells by using number cubes. And so calculate the average of the 8 values you institute.
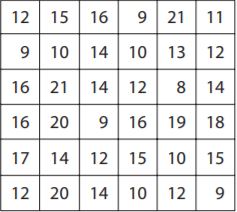
Answer: The average is xv.
Caption: We can roll a number cube twice and record each value. The first value will exist the row number and the 2nd will be the cavalcade number we repeat the process 8 times in society to get 8 ages from the grid. 12,x,21,ix,xviii,sixteen,14,20.
The mean is \(\frac{12+10+21+ix+18+16+14+20}{half dozen}
= \frac{120}{viii}\)
= 15
Question 12.
Communicating Mathematical Ideas
Describe how the size of a random sample affects how well it represents a population as a whole.
Respond: The bigger the size of the random sample, the more than probable it and so accurately represents the population.
10.ane Populations and Samples – Folio No. 329
Question 1.
A company uses a estimator to identify their 600 most loyal customers from its database and then surveys those customers to find out how they like their service. Identify the population and make up one's mind whether the sample is random or biased.
The sample is _______
Answer: The population is the customers in the company's database. The sample is biased because instead of surveying all of their customers, the company only surveyed their most loyal customers.
x.2 Making Inferences from a Random Sample
Question 2.
A academy has 30,330 students. In a random sample of 270 students, 18 speak three or more than languages. Predict the number of students at the university who speak 3 or more languages.
_______ students
Answer: 2022 students.
Caption: Let X be the number of students to speak iii or more languages, and so
xviii/270 = X/30,330
1/15 = 10/30,330
10= 2022.
10.three Generating Random Samples
A store receives a shipment of v,000 MP3 players. In a previous shipment of 5,000 MP3 players, 300 were defective. A store clerk generates random numbers to simulate a random sample of this shipment. The clerk lets the numbers 1 through 300 represent defective MP3 players, and the numbers 301 through v,000 correspond working MP3 players. The results are given.
13 2,195 three,873 525 900 167 1,094 ane,472 709 v,000
Question 3.
Based on the sample, how many of the MP3 players might the clerk predict would be defective?
_______ MP3's
Answer: yard MP3's.
Caption: Equally the two random numbers are 13 and 167 as they are less than 300 and thus correspond defective MP3 players. And the other 8 numbers are greater than 300 and represent working MP3 players. So the total number of randomly generated numbers is 10.
two/10 = X/5000
1/5 = 10/5000
X = k.
And then, nigh 1000 MP3 players are defective.
Question 4.
Can the manufacturer assume the prediction is valid? Explain.
_______
Answer: No.
Explanation: As the manufacturer cannot assume the prediction is valid. As the sample size of ten is likewise small-scale compared to the size of the shipment.
Essential Question
Question five.
How can you use random samples to solve real-world bug?
Respond: Nosotros tin can use random samples to make a prediction about the population that is too large to survey.
Selected Response – Page No. 330
Question ane.
A farmer is using a random sample to predict the number of broken eggs in a shipment of 3,000 eggs. Using a figurer, the farmer generates the post-obit random numbers. The numbers one–250 correspond cleaved eggs.
477 2,116 1,044 81 619 755 two,704 900 238 one,672 187 ane,509
Options:
a. 250 broken eggs
b. 375 cleaved eggs
c. 750 cleaved eggs
d. 900 broken eggs
Respond: 750 cleaved eggs.
Explanation: Iii random numbers are 81, 187, 238 which are less than 250 and correspond broken eggs, and then
3/12 = Ten/3000
1/4 = X/3000
4X = 3000
X= 750
Question ii.
A center schoolhouse has 490 students. Mae surveys a random sample of 60 students and finds that 24 of them have pet dogs. How many students are likely to have pet dogs?
Options:
a. 98
b. 196
c. 245
d. 294
Respond: 196.
Explanation: Permit the number of students is likely to have pet dogs be X, and then
24/60 = X/490
60X = 24×490
60X = 11,760
X = 196.
Question 3.
A pair of shoes that commonly costs $75 is on sale for $55. What is the percent decrease in the cost, to the nearest whole percent?
Options:
a. 20%
b. 27%
c. 36%
d. 73%
Answer: 27%
Caption: The percent decrease in the toll is \(\frac{75-55}{75}
= \frac{twenty}{75}\)
= 0.266= 27%
Question 4.
Which of the following is a random sample?
Options:
a. A radio DJ asks the first 10 listeners who call in if they liked the last vocal.
b. 20 customers at a craven restaurant are surveyed on their favorite food.
c. A polling organization numbers all registered voters, then generates 800 random integers. The polling organization interviews the 800 voters assigned those numbers.
d. Rebecca used an email poll to survey 100 students almost how frequently they employ the internet.
Answer:
A is biased considering it is a voluntary survey.
B is biased because only 20 customers surveyed on their favorite food.
C is a sample because that is random.
D is biased students using electronic mail more likely to use the net that students who don't use e-mail.
Question five.
Each jail cell in the table represents the number of people who work in one 25-square-block section of the town of Middleton. The mayor uses a random sample to estimate the boilerplate number of workers per block.
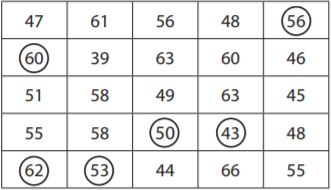
a. The circled numbers represent the mayor'south random sample. What is the mean number of workers in this sample?
______
Reply: The mean is 54.
Explanation: The mean is \(\frac{56+sixty+fifty+43+62+53}{half-dozen}
= \frac{324}{half-dozen}\)
= 54
Question 5.
b. Predict the number of workers in the entire 25-cake section of Middleton.
______
Answer: one,350.
Caption: As we know that the hateful is 54 per block, so for the entire 25 cake section, the number is 54×25= 1,350.
Summary:
We wish the data given in the Go Math Reply Key Grade seven Chapter x Random Samples & Populations is helpful for you. The primary aim of our team is to brand y'all understand the concepts and ameliorate your math skills. Learn the techniques and employ them in real-time this helps you lot to perform well in the exams. For whatsoever queries, y'all tin comment in the below comment box. All the All-time!!!
Source: https://ccssmathanswers.com/go-math-grade-7-answer-key-chapter-10-random-samples-and-populations/
0 Response to "Chapter 10 Review Test 5th Grade Answer Key"
Post a Comment